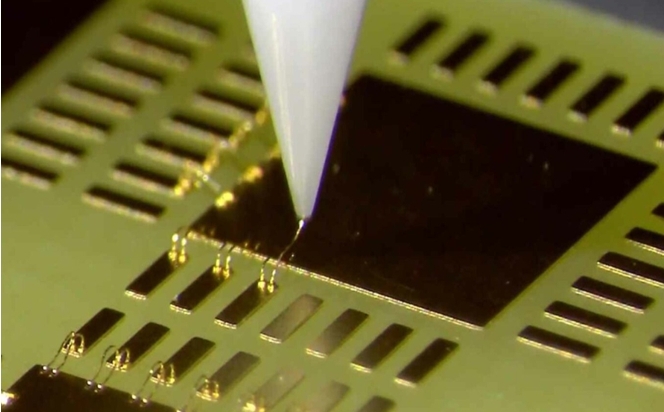
What is Wire Bonding?
Wire bonding is the process of making interconnection between the chip and the substrate or PCB. A significant development in PCB electronics is the concept of wire bonding. It is an important technology in electronics manufacturing in establishing reliable circuits using metallic wires such as gold, aluminum, and copper. The choice of wire bonding material heavily relies on the intended application, cost, reliability, and compatibility.
Wire bonding machines are highly automated, and equipped with a Pattern Recognition System (PRS) to be able to locate the chip bonding pads and PCB reference points for precise wire bonding. The PCB or substrate with the chip to be wire bonded must be clamped and secured in place through the vacuum. This is to ensure planarity and stability of the PCB and chip while bond formation takes place. A capillary is a tool that holds and bonds the wire during the process.
What are the Different Types of Wire Bonding?
Ultrasonic Bonding
Ultrasonic bonding is a popular wire bonding process that can be done at lower temperatures with the application of ultrasonic frequency. The ultrasonic energy is generated from a transducer that mechanically vibrates the capillary or bonding tool ranging from low to high frequencies. Aluminum is a common material in ultrasonic bonding wherein a wedge capillary tool is used to bond the metal. Briefly discussed below is the sequence of the ultrasonic bonding process:
- A downward force is applied to land the wire to the bond pad.
- Ultrasonic scrub helps achieve the desired wedge bond.
- A wire loop is formed, and the clamp is opened.
- A downward force is again applied to land the wire and create the stitch or second bond on the PCB or substrate.
- The wire is cut at the heel of the wedge.
Thermosonic Bonding
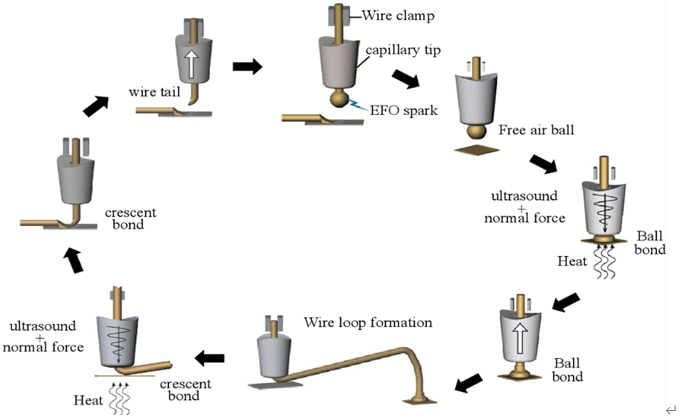
In thermosonic bonding, ultrasonic energy is applied to the capillary with wire while the substrate or pad is heated to a high temperature. Gold and copper can be used in thermosonic bonding. Refer to the following simplified steps in understanding this type of bonding:
- The wire is held in place by the capillary tool.
- The ball is formed by striking the wire with an EFO (Electric Flame-Off) spark.
- Capillary with wire lands on the chip pad
- Ultrasonic energy, heat, and pressure form the ball bond on the pad.
- A loop is formed as the capillary is lifted.
- Ultrasonic energy, heat, and pressure form the stitch bond on the PCB or substrate.
Thermocompression Bonding
Thermocompression bonding is somehow similar to thermosonic bonding except that ultrasonic energy is not applied during the process. Heat, time and pressure are the critical parameters that define the formation of the bond. The heat during interface bonding is realized through a heated capillary or a heated stage. The latest thermocompression bonders utilized both methods. Another difference with thermosonic technology is that thermocompression bonding employs higher force with a flatter ball dimension. The same sequence is applicable wherein a ball is first formed through an EFO spark and attached to the chip or substrate.
What are the Things to Consider during the Wire Bonding Process?
Wire Type and Size
Wire type and size must be carefully assessed to ensure proper wire bonding PCB. Wire type includes the type of material to be used and its corresponding purity and alloying composition. Improper choice of wire type and size may result in reliability failures. For fine-pitched devices, smaller wire sizes will be needed with higher sensitivity to swaying or shorting with adjacent wires.
Capillary Type
The capillary to be used plays a critical role in the PCB wire bonding process performance. Some features of the capillary such as the chamfer diameter and face angle dictate the ball and wedge formation during wire bonding. Wrong capillary geometry can cause serious problems such as bond smearing, oversized bonds, and broken welds or stitches.
Clean Surfaces
The surfaces to be wire bonded must be clean and free from contamination that may interfere with the bonding of the wire to the pads. Plasma cleaning of the surfaces is sometimes employed to clean and precondition the contact areas for effective wire bonding. Contaminated PCB wire bonding areas can lead to low wire pull and bond shear test results. For copper wire bonding, it is important to use forming gas or nitrogen to avoid oxidation.
I-tech electronics co.,ltd know how to keep pcb pad be clean, no dent ,no damaged…and is experienced to manufacture the pcbs.
Wirebond Machine Parameters
Major PCB wire bond parameters such as wire-bond force, power, and time must be optimized to achieve quality wire-bonded surfaces. Excessive power or force can lead to “cratering” or even cracking of wire bonding pads while lack of the same parameters can cause nonsticking and low pull test results. Design experiments and parameter screening are being conducted to know the acceptable window for force, power, and time.