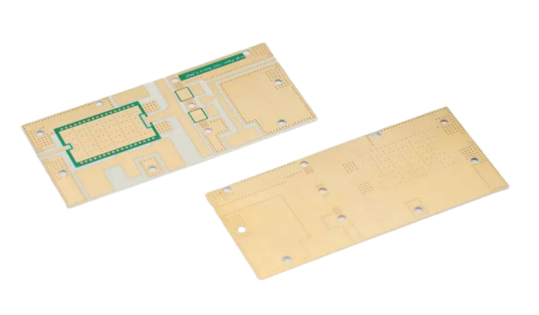
Embedded Copper Block (Coin) PCB Technology: Thermal Dissipation Characteristics and Process Optimization
1. Technical Background and Application Value
With the increasing demand for PCB thermal dissipation capacity in high-density electronic components and high-power devices, the industry has introduced embedded copper block (Coin)PCB technology. This technology utilizes the high thermal conductivity of copper blocks (thermal conductivity: 401 W/m·K) to rapidly transfer heat generated by internal components to the copper block, which then dissipates heat through air convection. The process involves: after completing the circuit layer fabrication and lamination of the PCB, creating mounting cavities via slot milling and wall metallization, and finally embedding the copper block into the slots. The copper block and PCB achieve physical fastening through embedding tolerance and electrical connection through copper plating, forming an efficient heat dissipation pathway. This article analyzes and optimizes the technology from three aspects—copper block design, dimensional compensation, and pressing control—to enhance the quality and reliability of PCB products.
2. Technical Classification and Thermal Advantages
According to the bonding method between the copper block and PCB, the technology can be divided into buried copper block(coin) PCB and embedded copper block(Coin) PCB:
Performance Comparison:
The embedded copper block design directly contacts the inner copper layers and external air, forming a "component-copper block-air" heat dissipation channel, which improves thermal efficiency by ~30% compared to the buried type. Additionally, the reduced process steps lower costs by 15–20%, offering broader application prospects. However, immature technology and process challenges easily cause reliability issues, limiting large-scale adoption.
3. Process Challenges and Failure Modes
The core process of embedded copper blocks—"slot milling-metallization-embedding"—faces critical technical challenges:
4. Process Optimization Solutions
(1) Copper Block Structure and Dimensional Design
(2) Flatness Control Technology
(3) Process Validation and Results
Through DFM simulation and mass production verification, the optimized process achieves:
5. Conclusion
Embedded copper block (Coin)PCB technology effectively addresses heat dissipation challenges in high-density electronic systems through structural and process optimizations. Future research should focus on micro-structured copper block surfaces (e.g., fin arrays) to enhance natural convection and lead-free plating processes for long-term reliability, enabling expansion into higher power density applications.
I-tech electronics co.,ltd provides pcbs with the advanced technologies for Embedded Copper Block(Coin)and Buried Copper Buried Copper block (Coin)